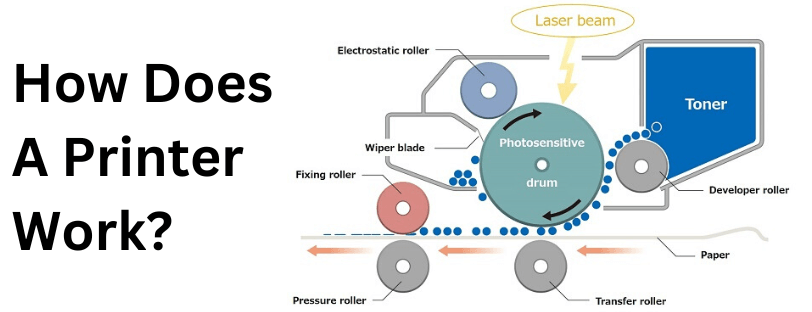
At a basic level, printers work by converting digital images and text into physical copies. This is done using a driver or specialized software designed to convert the file into a language the printer can understand. The image or text is then recreated on the page using a series of minuscule dots. The only real difference between various types of printers is the method by which the dots are transferred onto a page.
The are several printing technologies available. This includes Laser, Inkjet, Thermal, Dot Matrix and Solid Ink, but the most commonly produced and widely used are the laser and inkjet technologies.
We have seen an increase in Thermal usage in the last few years, but they are most heavily used in specific sectors.
Solid Wax Ink technology was created and patented by Xerox years ago. This is a unique, award-winning system, that uses a block of wax.
Dot Matrix printers were incredibly popular in the 80s but are often considered outdated these days.
How Does An Inkjet Printer Work?
Inkjet printers are one of the most common printer types, these are usually found in homes due to their more compact size, and in art studios thanks to a higher image print quality.
Inkjet printers feature a print head containing thousands of tiny precision holes referred to as “nozzles”. The nozzles drop or eject microscopic droplets of ink at high speed onto the paper loaded into the printer.
Inkjet printers use liquid ink produced either by a coloured dye or a liquid that contains solid pigments in suspension. As the print head moves horizontally in the machine, the paper passes through perpendicular to it.
As the page passes through, the nozzle in the print head is activated (usually by heat electrical current depending on the manufacturer) and a small drop of ink is ejected or sprayed out onto the page. This process is performed at high speed with thousands of droplets that form together to recreate the digital text or image that is being transferred onto the media. To the naked eye, the overall image looks to be solid because the dots are so tiny.
Parts Inside An Inkjet Print Engine
- Print Head
- Ink Cartridges
- Print Head Stepper Motor
- Belt
- Stabilizer Bar Rollers
- Paper Feed Stepper Motor
The Inkjet Printing Process
- An ink cartridge or tank supplies the printhead with the necessary inks
- The printhead starts to move across the page at high speeds
- Thousands of tiny ink drops are sprayed onto the page at high speeds in a horizontal motion
- The page moves through the printer under the moving printhead to create the print
- The final print is ejected into the output tray.
How Does A Laser Printer Work?
The laser printing process is arguably the most technically advanced method, especially when compared to the simplicity of Inkjet, but it’s still the most popular for text-based documents and office printing.
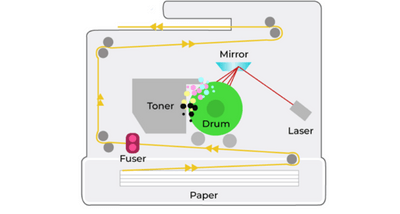
Laser and LED printers work in a similar way to inkjet in that the image is made up of lots of tiny dots, which, when viewed as a whole, appear to be a solid image. However, the method which is adopted for creating those tiny dots is very different. Where an inkjet uses liquid dots, a laser machine uses dots made up of toner – a fine powder of solid particles.
When compared with an inkjet or other method of printing, lasers are much more complex. These machines rely on many more stages during the process. In simple terms, the basic process uses a light source (laser/LED), drum and toner.
In order to create an image on the page, the drum is first charged and then the laser or LED is shone onto the drum in the outline of the intended image. The toner itself is attracted to areas of the drum that are not positively charged and a series of rollers transfer the powder from the toner cartridge and present it at the drum. The areas that are positively charged repel the toner and the area that is not attracting the toner particles which are pulled onto the drum and stick to the parts that make up the image. Paper is also transported to meet the drum, which, then, transfers the image across to the page itself.
Parts Inside A Laser Print Engine
- Toner Cartridge
- Drum Unit
- Laser
- Transfer Belt
- Fuser Unit
The Laser Printing Process
- The printer’s laser projects your print onto a drum.
- A drum then uses static electricity to attract the dry toner to the drum’s cylinder.
- The drum then rolls the toner onto the paper to create your print.
- The toner powder is melted and pressed onto the paper with heat from the fuser as it goes through a set of rollers.
- Your print comes out of the printer.
How Does A Dot Matrix Printer Work?
Dot Matrix printers, also known as “Impact Matrix devices” are an older type of printer, working similarly to a Typewriter. Originally they were a cost-effective printing option but were replaced by laser and inkjet printers for better quality and more versatility. Dot Matrix printers can still be found in some places, commonly harsh environments where print quality isn’t important and the carbon copy duplication can provide perfect copies in one print.
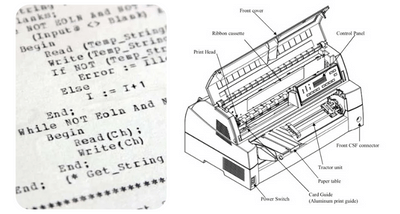
Dot matrix printers are made of a group of pins, which are used to print the characters on the page. You can choose from either 9 pins or 24 pins – 9 pins are usually the fastest option, meanwhile, 24 pins boast the highest resolution.
Dot Matrix printers, also known as “Impact Matrix devices” are an older type of printer. They work similarly to a Typewriter. Originally they were a cost-effective printing option but were replaced by laser and inkjet printers for better quality and more versatility. Dot Matrix printers can still be found in mechanic garages where print quality isn’t important and carbon copy duplication can provide perfect copies in one print.
Dot Matrix printers form a print by mechanically punching a pattern of ink dots out of a ribbon and onto the paper. The dots are formed by pins, carried in a printhead. Printheads include enough pins in to form a whole line of letters or numbers in one pass. Dot matrix printheads have 7, 9, 18 or 24 pins. Printers have had as many as 48 pins.
The paper moves vertically through the printer, but with a dot matrix printer this is on a steel roller, similar to a typewriter, the steel helps feed the paper and absorb energy from the printhead impact. Like an inkjet, the printhead sits on a carriage which scans across the page, impacting dots to build the finished print.
Parts Inside A Dot Matrix Print Engine
- Ink Ribbon
- Pins
- Printhead
- Print wires
- Listing Paper
- Solenoid
Dot Matrix Printing Process
- Listing paper is fed through the printer’s steel roller.
- The printhead scans across the page.
- Pins impact the ribbon to press a dot on the page in a vertical column to form the characters.
- As the paper is fed through the printer, and the print is complete the listing paper exits the printer.
How Does A Solid Ink Printer Work?
Solid Ink printers were great devices manufactured solely by Xerox. These had fantastic print quality and the highest print speeds. Using a crayon-like wax, which melts and is then projected onto the paper.
In 2016 the solid ink printers were discontinued and superseded by the Xerox VersaLink range
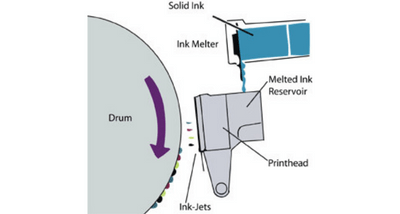
Solid ink is basically wax. When printing, these are then melted into liquid ink and then transferred onto the paper through a printhead. Solid Ink printers functioned similarly to inkjet printers.
Solid ink printers had a few advantages and disadvantages, their print quality had brilliant colour accuracy, especially for more vibrant prints. The use of wax would also create a glossy finish across the paper.
However, this did come with some disadvantages, a slow “warm-up time” was needed to melt the inks prior to the first page being printed, and they would also require a cool-down time before being moved so the inks could solidify again. Media type was also limited as the wax was unable to stick to photo paper, or speciality finished papers.
Parts Inside A Solid Wax Ink Print Engine
- Ink Sticks
- Heated Printhead
- Drum unit
- Ink-jets
Solid Ink Printing Process
- When the printer is turned on, a heater begins to melt the ink.
- Similar to a laser printer, the text or image is then projected onto the drum unit.
- The melted wax is dropped through a print head and onto the drum unit.
- The paper passes under the drum where the text or image is recreated on the page.
- The print comes out.
How Does A Thermal Printer Work?
There are 2 types of Thermal printers, primarily used for label printing, “Thermal Transfer” and “Direct Thermal”. The technology is also used in mobile receipt or document printers, and portable photo printers. These prints are created by special thermal paper passing under a print head full of pins heating the media below to generate the colour.
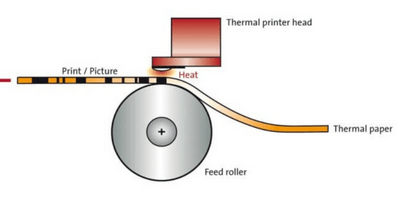
Thermal printers are predominantly used for label printing however, they are also used in standard A4 printers, usually built for mobility without the need for inks.
Thermal printers require a specialised “Thermal printer paper” to be used in the printer. This media has a dye coating over the paper which when heated changes colour (Most often to black)
Parts Inside A Thermal Print Engine
- Thermal paper/labels.
- Heated Printhead.
- Thermal Ribbon (For Thermal Transfer printers)
- Heated Printheads.
- Printhead pins
Thermal Printing Process
- Special thermal printer paper is loaded into the printer.
- Certain pins in the printhead are then heated up and dragged across the paper.
- When a heated pin comes in contact with the paper, it changes colour, creating the text or image.
- The print then leaves the printer.
And there we go, an explanation on how all the popular types of printer work. We hope you found this useful in your research for a new printer.
Need Help or More Information ?
If you need any further help or more information, reach out to us by leaving a comment below or through one of the many ways on our Contact Us page.
Alternatively you can contact us by Phone on 0161 308 5800 or by Live Chat on our main Website Monday to Friday and our team will be happy to help or answer with any questions you might have.
You can also find all the various ways to connect with Us at the bottom of this page. Please share this post if you found it helpful.


9 comments
Thumbs up to u
It really help
Very helpful. Your simple explanation helped me gain a basic understanding of the working principle of printers. It really matters.
Give printer and it’s working
Thank you
Very Helpfull.thank you
Thanks this really helped me with my essay!
Glad to hear so!
Thank you
The Printerbase Team
Comment I appreciate
Helpful and brief